|
|
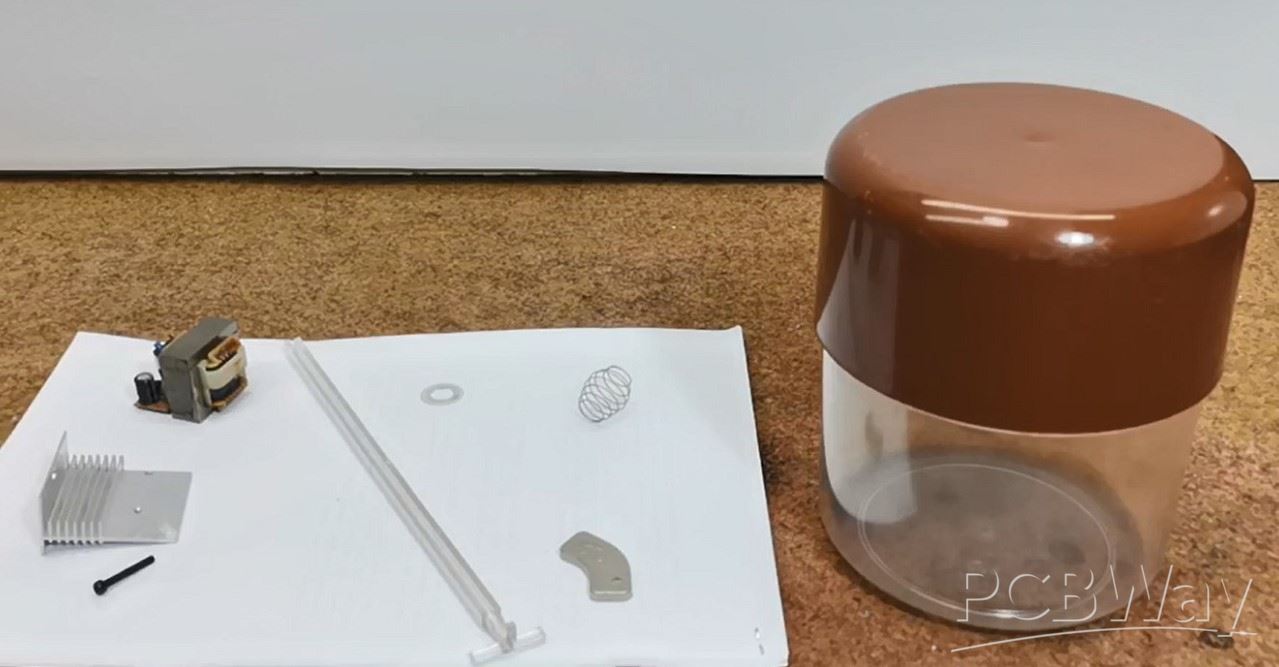
Neodimium magnet |
x 1 | |
|
|
Small E-type trafo |
x 1 | |
|
|
Aluminum plate with a thickness of about 1 mm |
x 1 | |
|
|
spring |
x 1 |

|
Soldering Iron Kit |
DIY Extremly Sensitive and cheap Geophone sensor for Earthquakes detecting
A geophone is a device used in geophysics to detect ground movement. It is specifically designed to measure seismic waves, which are produced by various sources, including earthquakes, and explosions. Typically consist of a mass suspended on a spring and a coil of wire within a magnetic field. When the ground shakes due to seismic activity, the mass moves, causing the coil to move within the magnetic field. This movement induces an electrical voltage in the coil.
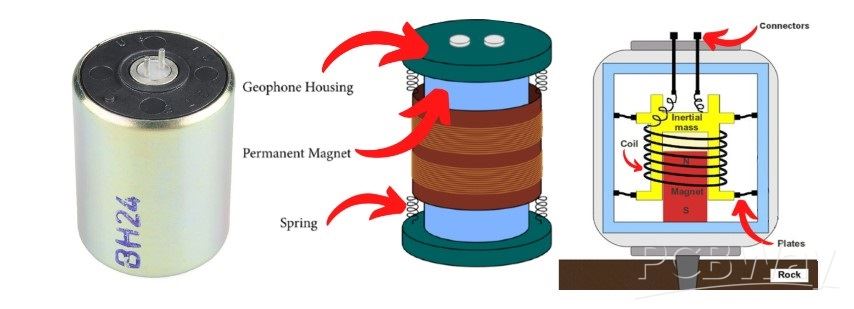
This signal is then amplified and filtered, then it is brought to a computer where it is visualized and logged for later analysis with specially designed software for this purpose. Unfortunately, these sensors are mostly unavailable to self-builders due to their high price. This time I will describe to you how to make such a sensor yourself for free from parts that can be found in any workshop.
However, the sensitivity does not lag behind commercial geophones at all. Even this sensor reacts to shocks in all possible directions which makes it incredibly practical, In other words, it replaces many different types of Geophones.
We only need a few components to make it.
- A plastic container, which serves to isolate the sensor from external influences, and it is preferable to be transparent (I use an ordinary plastic box for storing sugar or coffee)
- A small mains transformer taken out of an old electronic device with a power of a few watts
- Neodymium magnet (I use a magnet removed from an old PC hard drive)
- Aluminum or copper plate with a thickness of about 1 mm
- light spring
- and some nuts and bolts as needed

This project is sponsored by PCBWay. They has all the services you need to create your project at the best price, whether is a scool project, or complex professional project. On PCBWay you can share your experiences, or get inspiration for your next project. They also provide completed Surface mount SMT PCB assemblY service at a best price, and ISO9001 quality control. Visit pcbway.com for more services.

This time we will make only the Geophone, and in one of the following videos I will present you the method of making the signal amplifier, filter, as well as the A/D converter, where I will try to do it in the simplest way so that it is closer to a larger number of enthusiasts who potentially would like to make it. I will also describe how to set up a simple 24/7 monitoring software to work with this sensor.
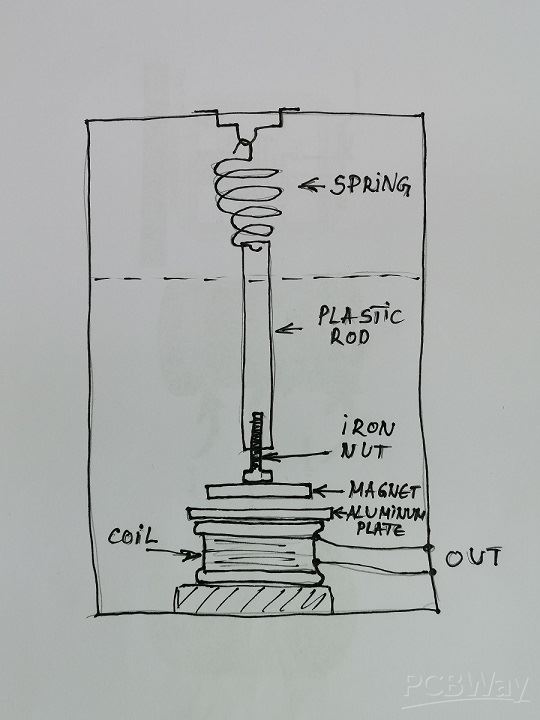
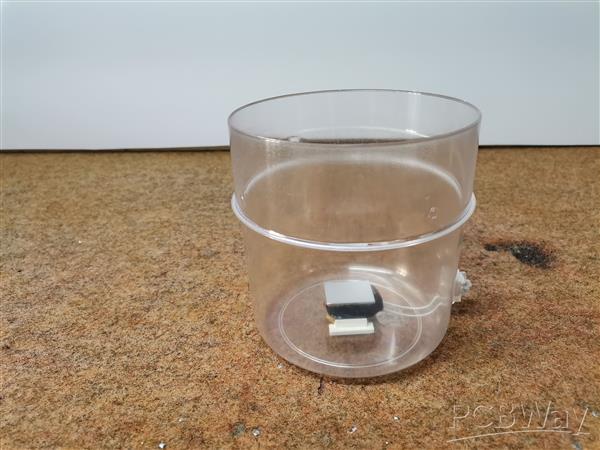
Now let's start making the sensor. First we need to disassemble the transformer, actually separate the windings from the metal part.

We need the primary winding, which contains a larger number of windings with a thinner wire. If the windings are covered with insulating tape, then with an ohmmeter we look for the winding with the highest resistance. Of course, we can also make this coil by winding 500 to 1500 turns of thin lacquered copper wire with a diameter of 0.1 mm

This winding need to be glued to the bottom of the box. Then we take the two leads from the winding with thin wires outside the box to a small terminal. Next, we glue the aluminum plate on top of the coil, which should have the same shape as the coil. This plate has the function of preventing the long-term oscillation of the magnet after the earthquake, and this process is called damping. When a magnetic field moves through a conductor the movement induces an eddy current in the conductor. The flow of electrons in the conductor immediately creates an opposing magnetic field which results in damping of the magnet.
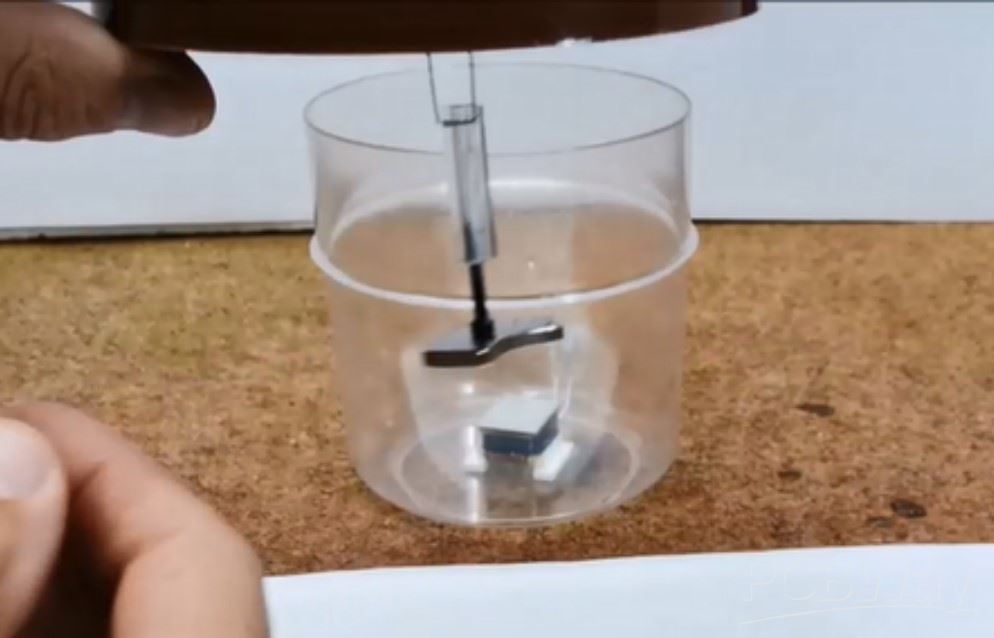

The length of the combination spring + rod + screw + magnet should be adjusted so that when the lid is closed, the magnet hangs approximately 1-1.5 mm above the aluminum plate.

As you can see, the sensor is sensitive to shocks from all directions and axes. During a vertical shock, which usually occurs near the epicenter, the spring reacts, and during a horizontal movement, the pendulum can move in all directions 360 degrees. Such sensors that respond in all axes are very expensive and are used only for professional purposes. This diy geophone can be mounted on the ground using spikes or other mechanisms to ensure good contact with the Earth's surface. In some cases, geophones are buried at varying depths.

And finally a short conclusion: This sensor is conceived as part of the final project, which will actually be a stand-alone seismometer and will display the relative intensity of the earthquake at the point of detection. Determining the direction, distance, and magnitude of an earthquake at the epicenter requires the interaction of at least three seismometers, but for this topic in another project. In the next video that I will promote soon, will be described the electronic part consisting of an amplifier, filter, A/D converter and PC software. Thus we will get a complete extremely cheap and sensitive home seismometer whose results (seismograms) are almost identical to those of the official seismological institutes. In the following, I will present to you several reports from my seismometer, which uses the above-described sensor.
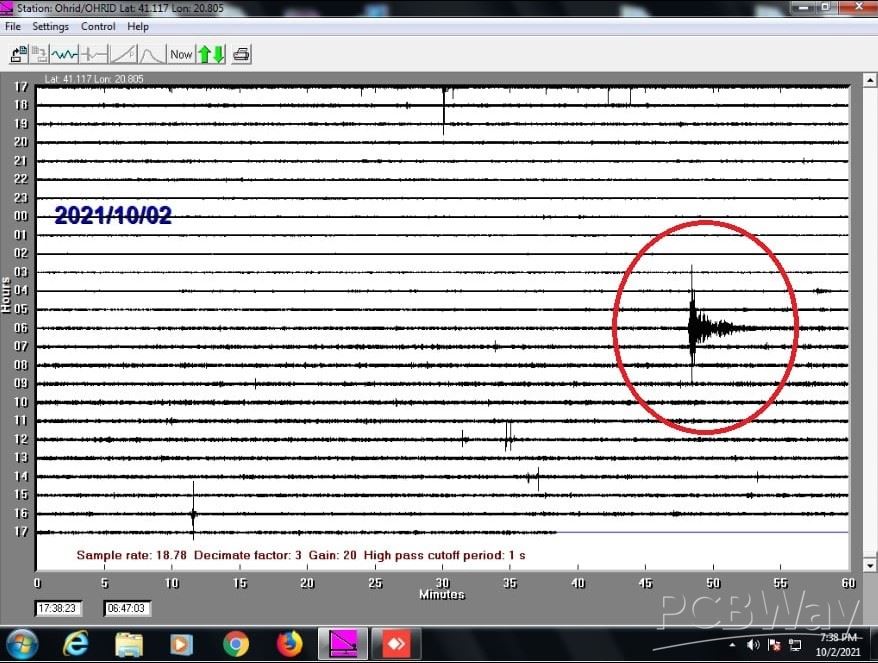
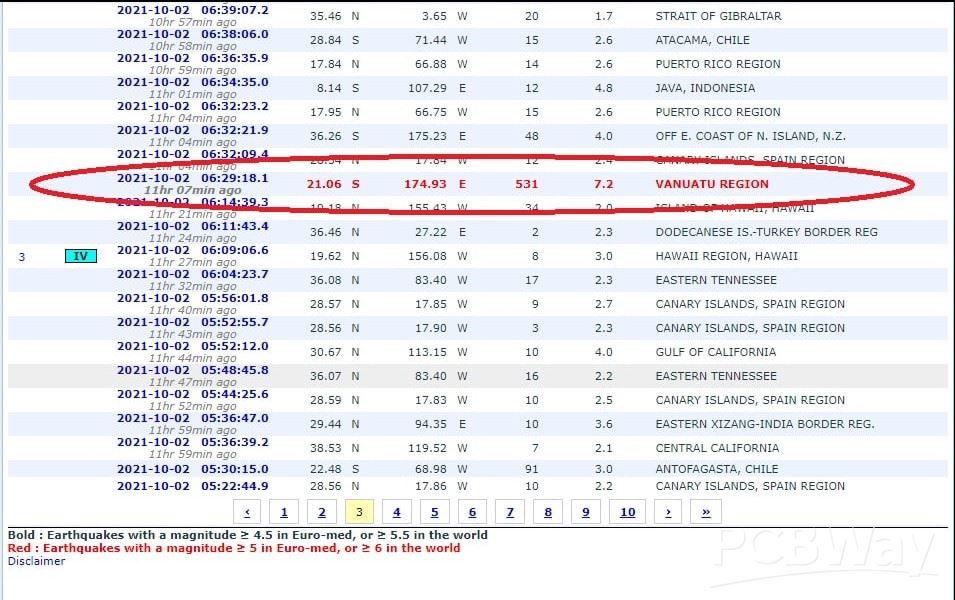
1. An earthquake with a magnitude of 7.2 on the Richter scale occurred 2 October 2021 at 08:29 h Ohrid time at a depth of 530 km on the island of Vanuatu, west of Australia in the Pacific Ocean. This is how this earth looks like, taken by my Seismometer at a distance of 15600 km from Ohrid

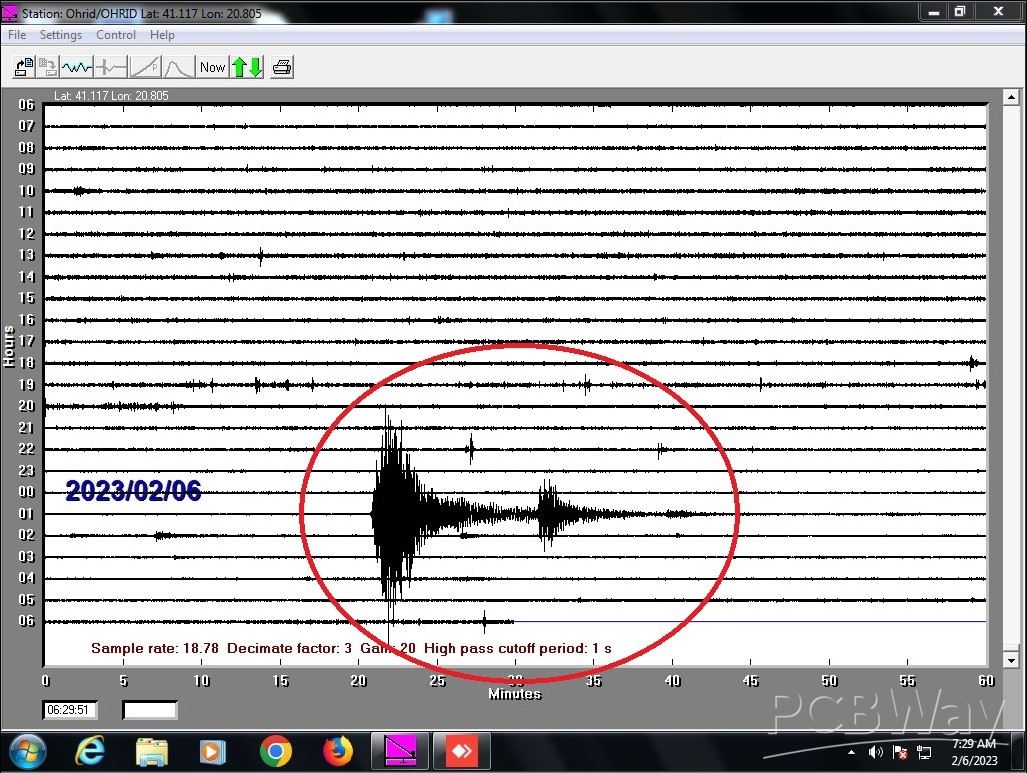
2. A very strong earthquake occurred at 01:17 UTC (6 February 2023), with a magnitude of 7.8 degrees on the Richter scale 37 km WNW of Gaziantep, Turkey
3.Local Earthquake with a magnitude of 3.8 on the Richter scale northeast of Korca, Albania 25 April 2023



DIY Extremly Sensitive and cheap Geophone sensor for Earthquakes detecting
- Comments(0)
- Likes(0)
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by Mirko Pavleski
More by Mirko Pavleski
-
 Arduino 3D Printed self Balancing Cube
Self-balancing devices are electronic devices that use sensors and motors to keep themselves balanc...
Arduino 3D Printed self Balancing Cube
Self-balancing devices are electronic devices that use sensors and motors to keep themselves balanc...
-
 DIY 5-Day Rainfall Forecast Device - ESP32 E-Paper Project
In several of my previous projects I have presented ways to make weather stations, but this time I ...
DIY 5-Day Rainfall Forecast Device - ESP32 E-Paper Project
In several of my previous projects I have presented ways to make weather stations, but this time I ...
-
 Build simple Retro Style VFO (Variable frequency oscillator) with Crowoanel 1.28 inch Round Display
Today I received a shipment with a Small round LCD display from Elecrow. The device is packed in tw...
Build simple Retro Style VFO (Variable frequency oscillator) with Crowoanel 1.28 inch Round Display
Today I received a shipment with a Small round LCD display from Elecrow. The device is packed in tw...
-
 Human vs Robot – Rock Paper Scissors with MyCobot 280 M5Stack
Today I received a package containing the few Elephant Robotics products. The shipment is well pack...
Human vs Robot – Rock Paper Scissors with MyCobot 280 M5Stack
Today I received a package containing the few Elephant Robotics products. The shipment is well pack...
-
 How to Build a Simple Audio Spectrum Analyzer with Adjustable Settings
An audio spectrum analyzer is an electronic device or software tool that measures and visually disp...
How to Build a Simple Audio Spectrum Analyzer with Adjustable Settings
An audio spectrum analyzer is an electronic device or software tool that measures and visually disp...
-
 How to Make a Digital Clock on a Vintage B&W TV using Arduino
These days I accidentally came across this small retro Black and White TV with a built-in Radio, so ...
How to Make a Digital Clock on a Vintage B&W TV using Arduino
These days I accidentally came across this small retro Black and White TV with a built-in Radio, so ...
-
 Build a $10 Function Generator with Frequency Meter for Your Lab
A function generator is a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate various types of elec...
Build a $10 Function Generator with Frequency Meter for Your Lab
A function generator is a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate various types of elec...
-
 From Unboxing to Coding - Radar Clock on Elecrow’s 2.1 HMI Display
Today I received a shipment with a large round LCD display from Elecrow. The device is packed in two...
From Unboxing to Coding - Radar Clock on Elecrow’s 2.1 HMI Display
Today I received a shipment with a large round LCD display from Elecrow. The device is packed in two...
-
 Making a Retro Analog NTP Clock with Unihiker K10 - Arduino IDE Tutorial
Some time ago I presented you a way to use standard Arduino libraries on the Unihiker k10 developme...
Making a Retro Analog NTP Clock with Unihiker K10 - Arduino IDE Tutorial
Some time ago I presented you a way to use standard Arduino libraries on the Unihiker k10 developme...
-
 Build a Cheap & Easy HF Preselector - Antenna Tuner
HF antenna preselector is an electronic device connected between an HF radio antenna, and a radio r...
Build a Cheap & Easy HF Preselector - Antenna Tuner
HF antenna preselector is an electronic device connected between an HF radio antenna, and a radio r...
-
 DIY Static Charge Monitor - Electrostatic Field Detector (Arduino & TL071)
A Static Charge Monitor also known as a Static Field Meter or Electrostatic Voltmeter is a device u...
DIY Static Charge Monitor - Electrostatic Field Detector (Arduino & TL071)
A Static Charge Monitor also known as a Static Field Meter or Electrostatic Voltmeter is a device u...
-
 XHDATA D-219 Radio Short Review with complete disassembly
Some time ago I received an offer from XHDATA to be one of the first test users of their new radio m...
XHDATA D-219 Radio Short Review with complete disassembly
Some time ago I received an offer from XHDATA to be one of the first test users of their new radio m...
-
 How to make Simplest ever Oscilloscope Clock
An oscilloscope clock is a unique and creative way to display the time using an oscilloscope, which...
How to make Simplest ever Oscilloscope Clock
An oscilloscope clock is a unique and creative way to display the time using an oscilloscope, which...
-
 DIY Digital Barograph with BME280 and ESP32 - 24 Hour Pressure Trends
A barograph is a self-recording barometer that continuously measures and records atmospheric pressu...
DIY Digital Barograph with BME280 and ESP32 - 24 Hour Pressure Trends
A barograph is a self-recording barometer that continuously measures and records atmospheric pressu...
-
 Build a Raspberry Pi Pico SDR Radio with Waterfall Display
Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that have traditional...
Build a Raspberry Pi Pico SDR Radio with Waterfall Display
Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that have traditional...
-
 DIY Magnet Polarity Detector - How to Identify Poles with a Hall Sensor from a PC Fan
Recently, while working on a project, I needed to determine the polarity of several permanent magne...
DIY Magnet Polarity Detector - How to Identify Poles with a Hall Sensor from a PC Fan
Recently, while working on a project, I needed to determine the polarity of several permanent magne...
-
 Light Meter Project - Making Dfrobot Unihiker K10 Work with Standard Arduino Libraries
The other day I received a shipment with a UNIHIKER K10 development board from DFRobot, which I rec...
Light Meter Project - Making Dfrobot Unihiker K10 Work with Standard Arduino Libraries
The other day I received a shipment with a UNIHIKER K10 development board from DFRobot, which I rec...
-
 DIY Simple Arduino Whack-a-Mole Game
A "Whack-a-Mole" game is a classic arcade-style game where moles pop up randomly from holes, and th...
DIY Simple Arduino Whack-a-Mole Game
A "Whack-a-Mole" game is a classic arcade-style game where moles pop up randomly from holes, and th...
-
-
AEL-2011 Power Supply Module
531 0 2 -
AEL-2011 50W Power Amplifier
493 0 2 -
-
-
Custom Mechanical Keyboard
701 0 0 -
Tester for Touch Screen Digitizer without using microcontroller
333 2 2 -
Audio reactive glow LED wristband/bracelet with NFC / RFID-Tags
314 0 1 -
-
-