
|
Soldering Iron Wire Welding Lead Roll |
|

|
Soldering iron |
|

|
arduino IDEArduino
|
Arduino hearing test device - Audiometer
An audiometer is a machine used for evaluating hearing acuity. They usually consist of an embedded hardware unit connected to a pair of headphones and a test subject feedback button. This device typically transmits pure tones to the headphones of the test subject at varying frequencies and intensities, and records the subject's responses to produce an audiogram of threshold sensitivity.
I recently took a hearing test in a professional facility, and I received the results in the form of an audiogram. I decided to try to make a similar device because the principle of operation of the device is quite simple. After a short research on the internet I found applications that use the sound card of the PC for this purpose, but my goal was to make a practical stand-alone device. I found idea for this type of device on the Arduino forums by a user named "cstram" and decided to make it with some modifications depending on the hardware I had at the time. In this case, the Arduino is an input-output unit that generates tones with different frequencies and intensity, and then displays the feedback results received from the person being tested, on a screen with a resolution of 8 x 8 pixels made up of 64 RGB LEDs. The screen displays two graphs in different colors, for the left and right ear.
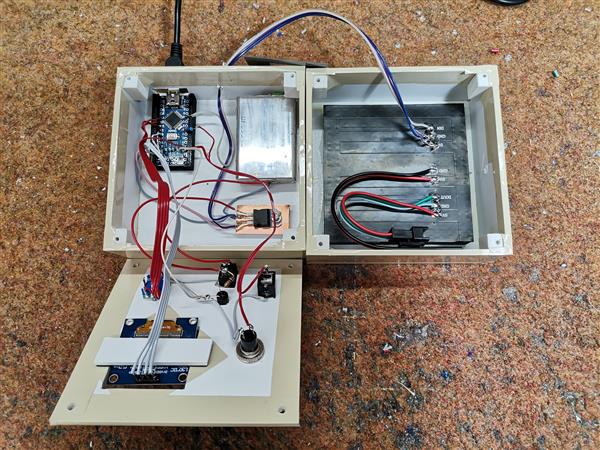

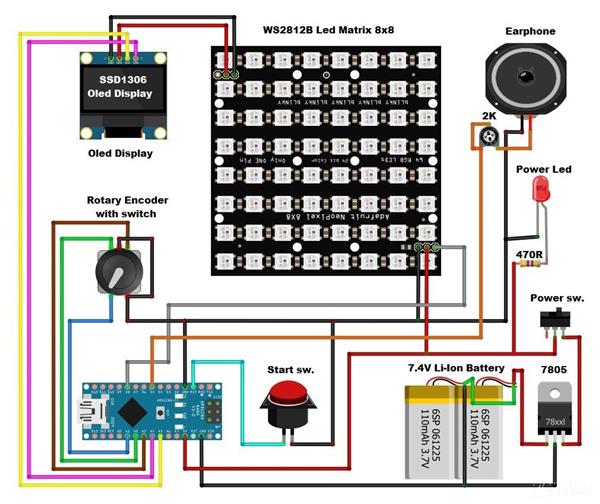
The device is relatively simple to build, and consists of several components:
- Arduino Nano microcontroller
- 8x8 matrix consist of 64 RGB Leds with buit-in WS2812 chip. For a more interesting visual impression, I made a 3D printed grid
- 128x64 Oled display with SSD1306 chip
- Rotary encoder
- push button
- female earphone jack
- and small earphones
The device is powered by two lithium batteries connected in series, and a 7805 5V voltage stabilizer is placed at its output. This time I neglected the battery control and charging circuit because that part has been described several times before.
If you want to make your own PCB for this project, or for any other electronic project, PCBway is a great choice for you. PCBway is one of the most experienced PCB manufacturing company in China in field of PCB prototype and fabrication. They have a large online community where you can find a Open Source projects, and you can also share your project there. From my personal experience I can tell you that on this community you can find many useful projects with alredy designed PCBs, from where you can place an order directly.

Now let's see how the device works in reality: When turning on the device, the first test frequency and the volume in decibels appear on the Oled screen. On the Matrix screen, the rows represent the sound volume in decibels and the columns represent the given frequency in Hertz. Now we put the earphone in one ear and using the rotary encoder we gradually increase the volume until we hear a sound. At that moment, we press the button, which remembers the result for the first frequency and switches to the next frequency, and thus we go to the end. When we finish with the last frequency, we switch the earphone to the other ear and repeat the procedure for all frequencies. Now the diodes will light up with a different color. At the end, the device plots the audiograms for both ears individually in red and blue. The display will give us all the information required. This will tell you the quality of you hearing at each frequency. The red color represents the left ear, while the blue color represents the right one. Let me mention that this is not a professional device and can be used for fun. However, if we calibrate it using a professional device, as I did, we can get quite a solid insight into the auditory capabilities of our hearing organs.
This is what a professional Audiogram looks like:

UPDATE:
A few days after I finished the project, I had access to the Bone Conduction Headset, which is used for Bone Conduction Testing.

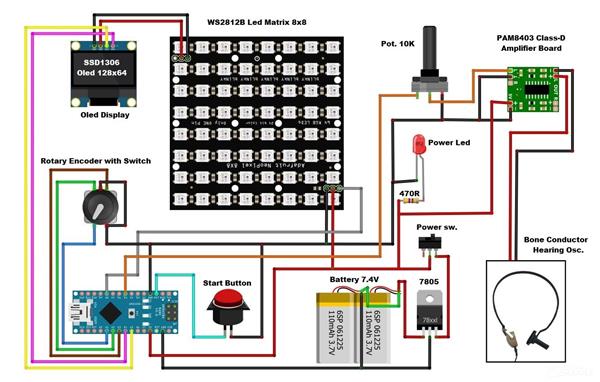
This is another type of pure-tone test that measures your inner ear’s response to sound. A conductor will be placed behind your ear; it will send tiny vibrations through the bone directly to the inner ear. This is different than the traditional version, which uses air to send audible sounds. If the results of this test are different than the pure-tone audiometry, your audiologist can use this information to determine your type of hearing loss. Determining the threshold should be done in the same way as obtaining the Air Conduction thresholds is performed. Bone-conduction measurements are normally restricted to the frequency range from 250 to 4000 Hz. With a small modification of the previously described device, I expanded its functionality, and after that Bone Conduction Testing can also be performed with it.
It is only necessary to add a small audio amplifier because the ohmic resistance of the test headset vibrator is only four ohms. I used a small inexpensive class D amplifier with a potentiometer which is quite suitable for this purpose.
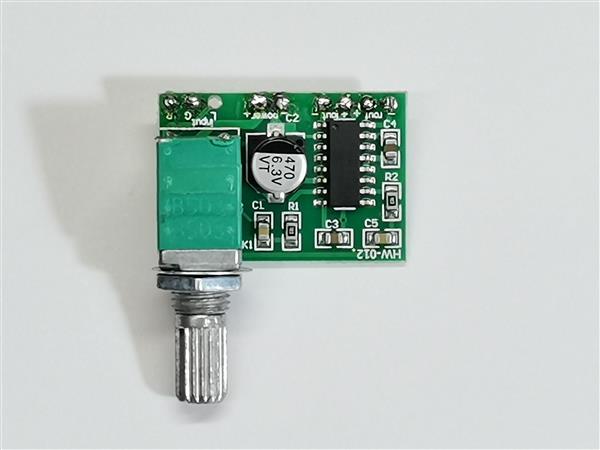

It is only necessary to bring the signal from headphones to the input of the amplifier. A Bone Conduction headset is connected to the output of the amplifier through a suitable connector. With the help of the potentiometer we can perform a precise calibration using a commercial device like this. So, as I mentioned before, the method of performing the test is exactly the same as in the previous case, only that instead of a headset, a Bone Conduction oscolator is placed on the bone behind the ear.
Finally, the device is installed in a suitable case made of PVC board and covered with colored wallpaper.
#include <Volume.h>
#include <RotaryEncoder.h>
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#include <OneButton.h>
#include <U8glib.h>
#define PIN 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel strip = Adafruit_NeoPixel(64, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
U8GLIB_SSD1306_128X64 u8g(U8G_I2C_OPT_NONE); // I2C / TWI
Volume vol;
// Change these two numbers to the pins connected to your encoder.
// Best Performance: both pins have interrupt capability
// Good Performance: only the first pin has interrupt capability
// Low Performance: neither pin has interrupt capability
// ----- Rotary settings here ----
#define ROTARYSTEPS 1
#define ROTARYMIN 1
#define ROTARYMAX 8
int lastPos = 0;
int exitFlag = 0;
// Setup a RoraryEncoder for pins A2 and A3:
RotaryEncoder encoder(A2, A3);
// Last known rotary position.
// Setup a new OneButton on pin A1.
OneButton button(A1, true);
int risultati[3][8];
int j=0;
int x=0;
int y=0;
int orecchio=1;
int pos = 1;
char db[9][10]=
{ "0 db",
"10 db",
"20 db",
"30 db",
"40 db",
"50 db",
"60 db",
"70 db",
"80 db"
};
char freq[8][10]
{ "125 Hz",
"250 Hz",
"500 Hz",
"1000 Hz",
"2000 Hz",
"3000 Hz",
"4000 Hz",
"8000 Hz"
};
int freqn[8][2]
{
125, 250, 500, 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, 8000
};
char ear[3][11]
{ "Volume:",
"Vol. Left:",
"Vol. Righ:"
};
void setup() {
strip.begin();
strip.show(); // Initialize all pixels to 'off'
encoder.setPosition(0 / ROTARYSTEPS); // start with the value of 0.
u8g.setColorIndex(1); // pixel on for Display
button.attachLongPressStop(longPressStop);
vol.begin(); // After calling this, delay() and delayMicroseconds will no longer work
// correctly! Instead, use vol.delay() and vol.delayMicroseconds() for
// the correct timing
vol.setMasterVolume(3.00); // Self-explanatory enough, right? Try lowering this value if the speaker is too loud! (0.00 - 1.00)
vol.delay(500);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Volume test with Encoder:");
}
void loop() {
button.tick();
encoder.tick();
int newPos = encoder.getPosition();
if (pos != newPos) {
if (newPos < ROTARYMIN) {
encoder.setPosition(ROTARYMIN / ROTARYSTEPS);
newPos = ROTARYMIN;
} else if (newPos > ROTARYMAX) {
encoder.setPosition(ROTARYMAX / ROTARYSTEPS);
newPos = ROTARYMAX;
}
Serial.print(newPos);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.println();
if (orecchio < 3){
u8g.firstPage();
do {
draw(ear[orecchio], 25, 16);
draw("Freq:", 15, 55);
draw(db[newPos], 40, 35);
draw(freq[x], 60, 55);
} while( u8g.nextPage() );
} else {
u8g.firstPage();
do {
draw(" FINAL GRAPH ", 0, 20);
draw(" EXECUTED ", 0, 50);
} while( u8g.nextPage() );
}
pos = newPos;
vol.tone (freqn[x],pos);
if (orecchio < 3)
for (j=(x*8); j<64;j++)
strip.setPixelColor(j, 0, 0, 0);
strip.show();
if ((x==0 or x==2 or x==4 or x==6) and orecchio==1)
strip.setPixelColor((pos-1)+(x*8), 10, 0, 0);
if ((x==1 or x==3 or x==5 or x==7) and orecchio==1)
strip.setPixelColor(((x+1)*8)-(pos), 10, 0, 0);
if ((x==0 or x==2 or x==4 or x==6) and orecchio==2)
strip.setPixelColor((pos-1)+(x*8), 0, 0, 10);
if ((x==1 or x==3 or x==5 or x==7) and orecchio==2)
strip.setPixelColor(((x+1)*8)-(pos), 0, 0, 10);
strip.show();
}
// vol.delay(10); // solo per test
}
// This function will be called once, when the button1 is released after beeing pressed for a long time.
void longPressStop() {
Serial.print("Button 1 longPress stop, x=");
// scanf("%d", &risultati[orecchio][pos]);
risultati[orecchio][x]=pos;
x=x+1;
pos=0;
encoder.setPosition(1);
if (x>7 and orecchio == 1) {
x=0;
orecchio =2;
}
if (x>7 and orecchio == 2) {
u8g.firstPage();
do {
draw(" PLEASE WAIT ", 0, 20);
draw(" FINAL GRAPH ", 0, 50);
} while( u8g.nextPage() );
strip.clear();
for (j=1; j<3;j++) {
Serial.println();
for (x=0; x<8;x++) {
if ((x==0 or x==2 or x==4 or x==6) and j==1)
strip.setPixelColor((risultati[j][x]-1)+(x*8), 10, 0, 0);
if ((x==1 or x==3 or x==5 or x==7) and j==1)
strip.setPixelColor(((x+1)*8)-(risultati[j][x]), 10, 0, 0);
if ((x==0 or x==2 or x==4 or x==6) and j==2)
if (strip.getPixelColor((risultati[j][x]-1)+(x*8)) == 0)
strip.setPixelColor((risultati[j][x]-1)+(x*8), 0, 0, 10);
else
strip.setPixelColor((risultati[j][x]-1)+(x*8), 10, 0, 10);
if ((x==1 or x==3 or x==5 or x==7) and j==2)
if (strip.getPixelColor(((x+1)*8)-(risultati[j][x])) == 0)
strip.setPixelColor(((x+1)*8)-(risultati[j][x]), 0, 0, 10);
else
strip.setPixelColor(((x+1)*8)-(risultati[j][x]), 10, 0, 10);
strip.show();
Serial.print(risultati[j][x]);
Serial.print(", ");
vol.delay(1000);
}
}
x=0;
orecchio = 3;
}
Serial.println(x);
Serial.print("Ear = ");
Serial.println(orecchio);
} // longPressStop1
void draw(char* parola, int posx, int posy) {
// graphic commands to redraw the complete screen should be placed here
u8g.setFont(u8g_font_unifont);
//u8g.setFont(u8g_font_osb21);
u8g.drawStr( posx, posy, parola);
}
Arduino hearing test device - Audiometer
*PCBWay community is a sharing platform. We are not responsible for any design issues and parameter issues (board thickness, surface finish, etc.) you choose.

Raspberry Pi 5 7 Inch Touch Screen IPS 1024x600 HD LCD HDMI-compatible Display for RPI 4B 3B+ OPI 5 AIDA64 PC Secondary Screen(Without Speaker)
BUY NOW- Comments(0)
- Likes(1)
-
 Stan
Mar 09,2023
Stan
Mar 09,2023
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by Mirko Pavleski
More by Mirko Pavleski
-
 Arduino 3D Printed self Balancing Cube
Self-balancing devices are electronic devices that use sensors and motors to keep themselves balanc...
Arduino 3D Printed self Balancing Cube
Self-balancing devices are electronic devices that use sensors and motors to keep themselves balanc...
-
 Build a 5-Day forecast Raspberry Pi Weather Dashboard (Step-by-Step)
Recently in one of my previous videos,I introduced you to the 7 inch Elecrow Pi Terminal and how to...
Build a 5-Day forecast Raspberry Pi Weather Dashboard (Step-by-Step)
Recently in one of my previous videos,I introduced you to the 7 inch Elecrow Pi Terminal and how to...
-
 ESP32 Aneroid Barometer using Squareline Studio and LVGL on CrowPanel Round display
A barometer is a scientific instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure. Rising Pressure genera...
ESP32 Aneroid Barometer using Squareline Studio and LVGL on CrowPanel Round display
A barometer is a scientific instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure. Rising Pressure genera...
-
 LINAMP Project – Winamp-Style Audio Front Panel on Raspberry Pi 5
Winamp is one of the most iconic and historically significant digital media players ever created. I...
LINAMP Project – Winamp-Style Audio Front Panel on Raspberry Pi 5
Winamp is one of the most iconic and historically significant digital media players ever created. I...
-
 Retro Style radio with CrowPanel 2.1inch round Display (TEA5767)
Some time ago I presented you a clock project with CrowPanel 2.1inch-HMI ESP32 Rotary Display 480*4...
Retro Style radio with CrowPanel 2.1inch round Display (TEA5767)
Some time ago I presented you a clock project with CrowPanel 2.1inch-HMI ESP32 Rotary Display 480*4...
-
 Pi-Pico RX - SDR Radio with New Firmware and Features
A few months ago I presented you a wonderful SDR radio project by DawsonJon 101 Things. In short, i...
Pi-Pico RX - SDR Radio with New Firmware and Features
A few months ago I presented you a wonderful SDR radio project by DawsonJon 101 Things. In short, i...
-
 How to make simple Variable HIGH VOLTAGE Power Supply
High Voltage Power Supply is usually understood as a device that is capable of generating a voltage...
How to make simple Variable HIGH VOLTAGE Power Supply
High Voltage Power Supply is usually understood as a device that is capable of generating a voltage...
-
 DIY 5-Day Rainfall Forecast Device - ESP32 E-Paper Project
In several of my previous projects I have presented ways to make weather stations, but this time I ...
DIY 5-Day Rainfall Forecast Device - ESP32 E-Paper Project
In several of my previous projects I have presented ways to make weather stations, but this time I ...
-
 Build simple Retro Style VFO (Variable frequency oscillator) with Crowoanel 1.28 inch Round Display
Today I received a shipment with a Small round LCD display from Elecrow. The device is packed in tw...
Build simple Retro Style VFO (Variable frequency oscillator) with Crowoanel 1.28 inch Round Display
Today I received a shipment with a Small round LCD display from Elecrow. The device is packed in tw...
-
 Human vs Robot – Rock Paper Scissors with MyCobot 280 M5Stack
Today I received a package containing the few Elephant Robotics products. The shipment is well pack...
Human vs Robot – Rock Paper Scissors with MyCobot 280 M5Stack
Today I received a package containing the few Elephant Robotics products. The shipment is well pack...
-
 How to Build a Simple Audio Spectrum Analyzer with Adjustable Settings
An audio spectrum analyzer is an electronic device or software tool that measures and visually disp...
How to Build a Simple Audio Spectrum Analyzer with Adjustable Settings
An audio spectrum analyzer is an electronic device or software tool that measures and visually disp...
-
 How to Make a Digital Clock on a Vintage B&W TV using Arduino
These days I accidentally came across this small retro Black and White TV with a built-in Radio, so ...
How to Make a Digital Clock on a Vintage B&W TV using Arduino
These days I accidentally came across this small retro Black and White TV with a built-in Radio, so ...
-
 Build a $10 Function Generator with Frequency Meter for Your Lab
A function generator is a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate various types of elec...
Build a $10 Function Generator with Frequency Meter for Your Lab
A function generator is a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate various types of elec...
-
 From Unboxing to Coding - Radar Clock on Elecrow’s 2.1 HMI Display
Today I received a shipment with a large round LCD display from Elecrow. The device is packed in two...
From Unboxing to Coding - Radar Clock on Elecrow’s 2.1 HMI Display
Today I received a shipment with a large round LCD display from Elecrow. The device is packed in two...
-
 Making a Retro Analog NTP Clock with Unihiker K10 - Arduino IDE Tutorial
Some time ago I presented you a way to use standard Arduino libraries on the Unihiker k10 developme...
Making a Retro Analog NTP Clock with Unihiker K10 - Arduino IDE Tutorial
Some time ago I presented you a way to use standard Arduino libraries on the Unihiker k10 developme...
-
 Build a Cheap & Easy HF Preselector - Antenna Tuner
HF antenna preselector is an electronic device connected between an HF radio antenna, and a radio r...
Build a Cheap & Easy HF Preselector - Antenna Tuner
HF antenna preselector is an electronic device connected between an HF radio antenna, and a radio r...
-
 DIY Static Charge Monitor - Electrostatic Field Detector (Arduino & TL071)
A Static Charge Monitor also known as a Static Field Meter or Electrostatic Voltmeter is a device u...
DIY Static Charge Monitor - Electrostatic Field Detector (Arduino & TL071)
A Static Charge Monitor also known as a Static Field Meter or Electrostatic Voltmeter is a device u...
-
 XHDATA D-219 Radio Short Review with complete disassembly
Some time ago I received an offer from XHDATA to be one of the first test users of their new radio m...
XHDATA D-219 Radio Short Review with complete disassembly
Some time ago I received an offer from XHDATA to be one of the first test users of their new radio m...
-
A Compact Charging Breakout Board For Waveshare ESP32-C3
488 3 4 -
AI-driven LoRa & LLM-enabled Kiosk & Food Delivery System
495 2 0 -
-
-
-
ESP32-C3 BLE Keyboard - Battery Powered with USB-C Charging
689 0 1 -
-
mammoth-3D SLM Voron Toolhead – Manual Drill & Tap Edition
675 0 1 -
-
AEL-2011 Power Supply Module
1350 0 2 -
AEL-2011 50W Power Amplifier
1229 0 2















































