|
|
RP2040-ZEROwaveshare
|
x 1 | |
|
|
GPS-NEO6M |
x 1 | |
|
|
TFT ST7735S |
x 1 | |
|
|
Rotary Encoder Module |
x 1 |

|
Soldering Iron Kit |
|

|
CircuitPythonCircuitPython
|
Building a GPS Speedometer with RP2040-Zero
Build a Feature-Packed GPS Speedometer with an RP2040
This project guide will walk you through building a multi-function GPS speedometer and trip computer using an RP2040 microcontroller. It leverages a GPS module for real-time data and presents it on a color display through a clean, multi-page interface.
Instead of a simple speed readout, this device provides five distinct data screens you can cycle through with a rotary encoder. It’s a practical tool for anyone who wants detailed metrics on their journey.
To be clear, this isn't a turn-by-turn navigator; it's a powerful data-gathering tool that uses GPS to provide rich information about your movement.
The five data pages are:
- Velocity: Shows current speed, with smaller readouts for peak speed, average speed, and total distance.
- Distance: Focuses on total distance traveled, elapsed time, and current speed.
- Analytics: A trip summary page showing average speed, total distance, and duration.
- Chronos: An elapsed time display, useful for timing runs or trips.
- Telemetry: A raw data view showing live satellite count, latitude, longitude, and altitude.
Use Cases
This device is a flexible data logger suitable for various activities:
- Cycling/E-biking: A compact, custom dashboard for your handlebars.
- Driving: A secondary display for trip statistics, independent of the car's built-in computer.
- Hiking/Boating: Track key metrics like distance, time, and coordinates.
- A Learning Platform: An excellent project for getting hands-on experience with CircuitPython, GPS modules, SPI displays, and UI design.
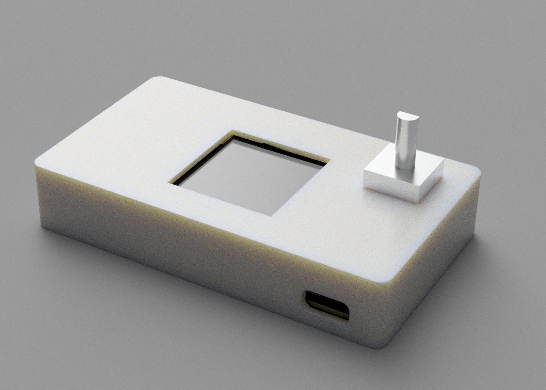
The Build: Hardware and Assembly
First, gather the necessary components.
Parts List
- Microcontroller: Waveshare RP2040-Zero - A compact RP2040 board with a USB-C connector.
- Display: 1.44" ST7735R 128x128 SPI TFT Display - A common color display compatible with the provided code.
- GPS Module: NEO-6M GPS Module (commonly found on a GY-NEO6MV2 breakout).
- Input: Rotary Encoder Module with Push-button for menu navigation and data reset.
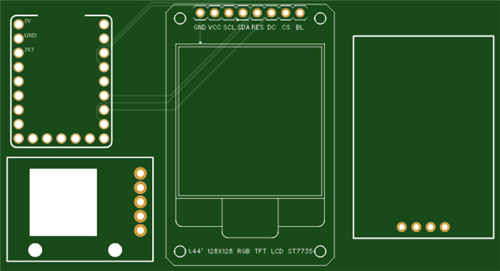
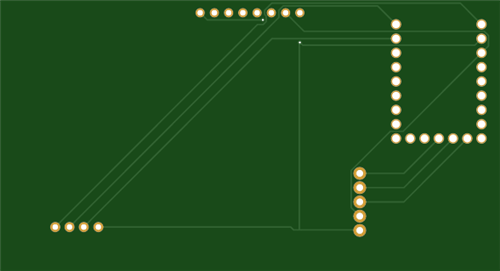
- PCB: A custom-designed PCB is recommended for a durable and clean build. Alternatively, you can use perfboard and wires.
Assembly and Wiring
The code specifies all pin connections. The main task is to create reliable connections between the modules and the RP2040.
Wiring Table:
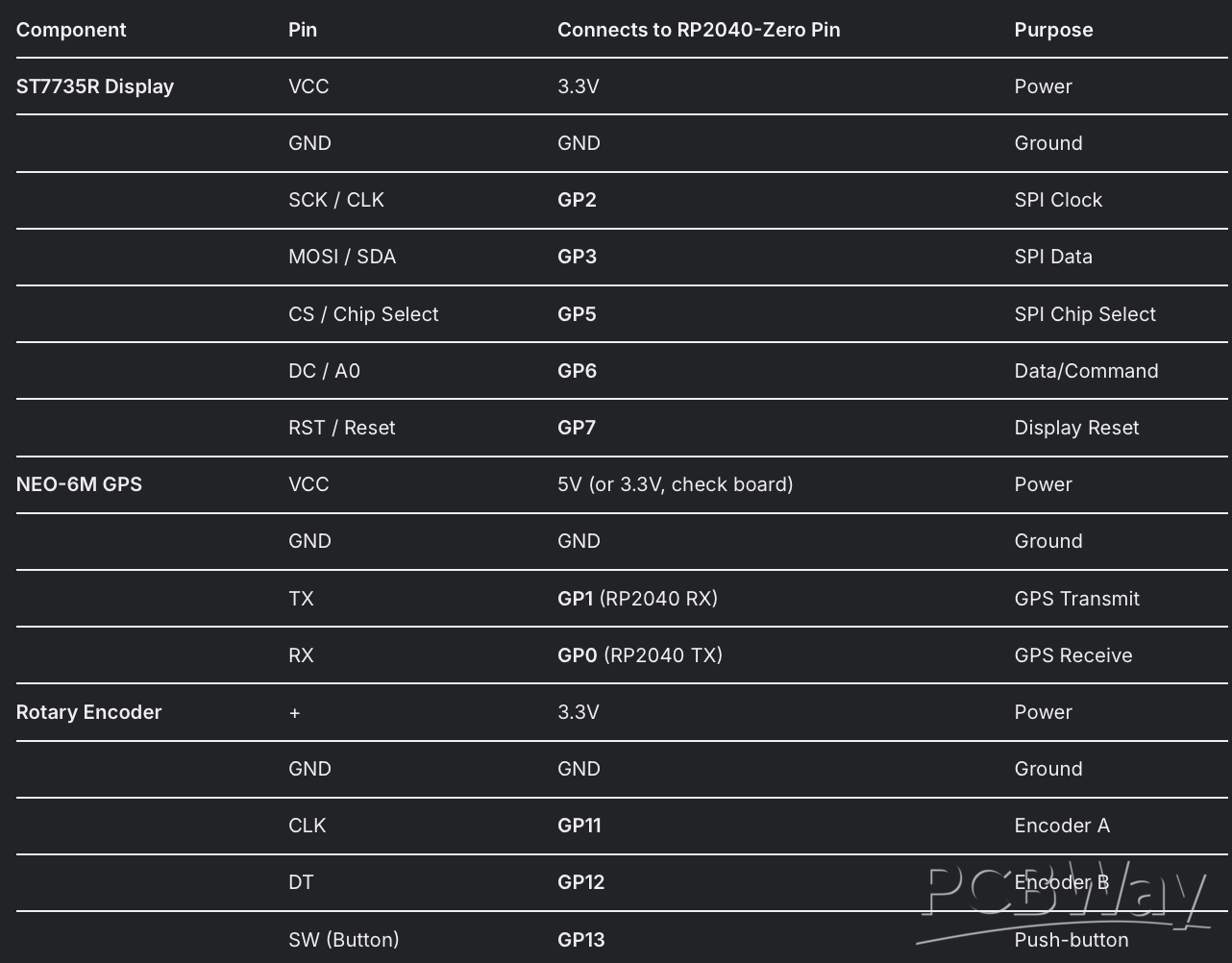
Soldering Steps:
- Secure the PCB.
- Carefully solder the RP2040-Zero to its footprint.
- Solder the display, GPS module, and rotary encoder to their designated pads, ensuring correct pin orientation.
- Inspect all solder joints for bridges or cold joints before powering on.
Software Setup and Code Upload
The project runs on CircuitPython, which simplifies the process of getting code onto the microcontroller.
Step 1: Install CircuitPython on the RP2040-Zero
- Download the latest .UF2 file for the Waveshare RP2040-Zero from the official CircuitPython website.
- Press and hold the BOOTSEL button on the RP2040-Zero and connect it to your computer. It will mount as a USB drive named RPI-RP2.
- Drag the downloaded .UF2 file onto the RPI-RP2 drive. The board will reboot and a new drive named CIRCUITPY will appear.
Step 2: Install Required Libraries
- Libraries provide the necessary drivers for the hardware. You must copy them into the lib folder on the CIRCUITPY drive.
- Download the Adafruit CircuitPython Library Bundle for your version of CircuitPython.
- Unzip the bundle.
- From the unzipped lib folder, find and copy the following files/folders to the lib folder on your CIRCUITPYdrive:
- adafruit_display_text (folder)
- adafruit_st7735r.mpy (file)
- adafruit_gps.mpy (file)
- adafruit_display_shapes (folder)
- adafruit_bus_device (folder)
- fourwire.mpy (file)
Note: The rotaryio, digitalio, busio, displayio, and board libraries are built into CircuitPython and do not need to be installed.
Step 3: Upload the Project Code
- Copy the full Python script provided.
- Paste it into a code editor (e.g., VS Code, Mu, Thonny).
- Save the file with the exact name code.py.
- Copy this code.py file to the root directory of the CIRCUITPY drive.
- The board will automatically restart and run the script. The display should initialize. For the first run, place the GPS module where it has a clear view of the sky to acquire a satellite fix.
How It Works and Next Steps
Once running, the device is simple to operate:
- Turn the rotary encoder to cycle through the five data pages.
- Press the rotary encoder's button to reset the trip data (distance, time, peak speed).
This project serves as a robust starting point. You can easily modify the code to change the color schemes, adjust the UI layout, add new data pages, or implement features like logging trip data to the RP2040's flash memory.
import board
import busio
import digitalio
import rotaryio
import displayio
import terminalio
import time
import math
from adafruit_display_text import label
from adafruit_st7735r import ST7735R
from adafruit_gps import GPS
from adafruit_display_shapes.rect import Rect
from adafruit_display_shapes.circle import Circle
from adafruit_display_shapes.line import Line
from adafruit_display_shapes.roundrect import RoundRect
from adafruit_display_shapes.polygon import Polygon
# Handle FourWire import for compatibility
try:
from fourwire import FourWire
except ImportError:
from displayio import FourWire
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Release any previous displays to free SPI pins
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
displayio.release_displays()
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Configuration & Wiring
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Display (ST7735S, 128x128)
spi = busio.SPI(board.GP2, board.GP3)
cs_pin = board.GP5
dc_pin = board.GP6
reset_pin = board.GP7
# GPS (GY-GPS6MV2)
uart = busio.UART(board.GP0, board.GP1, baudrate=9600, timeout=10)
gps = GPS(uart, debug=False)
gps.send_command(b"PMTK314,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0")
gps.send_command(b"PMTK220,1000")
# Rotary encoder
encoder = rotaryio.IncrementalEncoder(board.GP11, board.GP12)
button = digitalio.DigitalInOut(board.GP13)
button.switch_to_input(pull=digitalio.Pull.UP)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Premium Color Palette & Constants
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
SCREEN_WIDTH = 128
SCREEN_HEIGHT = 128
# Premium automotive-inspired color scheme
COLOR_NIGHT_BLACK = 0x0A0A0F
COLOR_DEEP_BLUE = 0x0F1419
COLOR_ELECTRIC_BLUE = 0x00D4FF
COLOR_NEON_GREEN = 0x39FF14
COLOR_AMBER = 0xFFB000
COLOR_CRIMSON = 0xFF0844
COLOR_PLATINUM = 0xE5E4E2
COLOR_SILVER = 0xB8B8B8
COLOR_CHARCOAL = 0x2A2A2A
COLOR_ACCENT_PURPLE = 0x9B59B6
COLOR_WARM_WHITE = 0xFFF8DC
COLOR_COOL_GRAY = 0x404040
COLOR_DARK_OVERLAY = 0x1A1A1A
# Page configurations with premium themes
PAGES = [
{
"name": "VELOCITY",
"color": COLOR_ELECTRIC_BLUE,
"accent": COLOR_NEON_GREEN,
"bg": COLOR_DEEP_BLUE,
"icon": "▲"
},
{
"name": "DISTANCE",
"color": COLOR_NEON_GREEN,
"accent": COLOR_ELECTRIC_BLUE,
"bg": COLOR_NIGHT_BLACK,
"icon": "●"
},
{
"name": "ANALYTICS",
"color": COLOR_AMBER,
"accent": COLOR_CRIMSON,
"bg": COLOR_CHARCOAL,
"icon": "◆"
},
{
"name": "CHRONOS",
"color": COLOR_CRIMSON,
"accent": COLOR_AMBER,
"bg": COLOR_DEEP_BLUE,
"icon": "⧗"
},
{
"name": "TELEMETRY",
"color": COLOR_ACCENT_PURPLE,
"accent": COLOR_ELECTRIC_BLUE,
"bg": COLOR_NIGHT_BLACK,
"icon": "◎"
}
]
NUM_PAGES = len(PAGES)
# Animation constants
ANIMATION_SPEED = 0.05
FADE_STEPS = 8
SLIDE_PIXELS = 4
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Advanced Helper Functions
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
def haversine(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2):
"""Calculate distance in meters between two lat/lon points."""
R = 6371000
phi1, phi2 = math.radians(lat1), math.radians(lat2)
dphi = math.radians(lat2 - lat1)
dlambda = math.radians(lon2 - lon1)
a = math.sin(dphi/2)**2 + math.cos(phi1)*math.cos(phi2)*math.sin(dlambda/2)**2
return 2 * R * math.atan2(math.sqrt(a), math.sqrt(1 - a))
def format_time(seconds):
"""Format time with dynamic precision"""
if seconds < 3600:
m = int(seconds // 60)
s = int(seconds % 60)
return f"{m:02d}:{s:02d}"
else:
h = int(seconds // 3600)
m = int((seconds % 3600) // 60)
s = int(seconds % 60)
return f"{h:02d}:{m:02d}:{s:02d}"
def format_coordinate(value, is_latitude=True):
"""Format coordinates with proper precision"""
if value is None:
return "ACQUIRING..."
direction = "N" if value >= 0 else "S" if is_latitude else "E" if value >= 0 else "W"
return f"{abs(value):.5f}°{direction}"
def log_gps_telemetry(gps_obj):
"""Advanced GPS telemetry logging"""
timestamp = time.monotonic()
if gps_obj.has_fix:
print(f"\n╔══ GPS TELEMETRY [{timestamp:.1f}s] ══╗")
print(f"║ POSITION: {gps_obj.latitude:.6f}, {gps_obj.longitude:.6f}")
print(f"║ VELOCITY: {gps_obj.speed_knots:.2f} knots ({gps_obj.speed_knots*1.852:.1f} km/h)")
print(f"║ HEADING: {gps_obj.track_angle_deg:.1f}° True")
print(f"║ ALTITUDE: {gps_obj.altitude_m:.1f}m MSL")
print(f"║ ACCURACY: {gps_obj.satellites} sats, HDOP {gps_obj.horizontal_dilution}")
print(f"║ QUALITY: Fix Type {gps_obj.fix_quality}")
print(f"╚══════════════════════════════════════╝")
else:
print(f"\n⚠ GPS ACQUISITION [{timestamp:.1f}s] - Satellites: {gps_obj.satellites or 0}")
def create_gradient_rect(x, y, width, height, color1, color2, steps=8):
"""Create gradient effect using multiple rectangles"""
group = displayio.Group()
step_height = height // steps
for i in range(steps):
# Simple gradient interpolation
factor = i / (steps - 1)
r1, g1, b1 = (color1 >> 16) & 0xFF, (color1 >> 8) & 0xFF, color1 & 0xFF
r2, g2, b2 = (color2 >> 16) & 0xFF, (color2 >> 8) & 0xFF, color2 & 0xFF
r = int(r1 + (r2 - r1) * factor)
g = int(g1 + (g2 - g1) * factor)
b = int(b1 + (b2 - b1) * factor)
gradient_color = (r << 16) | (g << 8) | b
rect_y = y + i * step_height
rect_height = step_height + (1 if i == steps - 1 else 0) # Handle remainder
rect = Rect(x, rect_y, width, rect_height, fill=gradient_color)
group.append(rect)
return group
def create_modern_button(x, y, width, height, color, text="", text_color=COLOR_WARM_WHITE):
"""Create modern button with glow effect"""
button_group = displayio.Group()
# Calculate safe radius (max half of smaller dimension)
safe_radius = min(width // 2, height // 2, 3)
# Outer glow
if safe_radius > 0:
glow = RoundRect(x-1, y-1, width+2, height+2, safe_radius, fill=color, stroke=color)
else:
glow = Rect(x-1, y-1, width+2, height+2, fill=color, stroke=color)
button_group.append(glow)
# Main button
if safe_radius > 0:
main_btn = RoundRect(x, y, width, height, safe_radius, fill=COLOR_NIGHT_BLACK, stroke=color)
else:
main_btn = Rect(x, y, width, height, fill=COLOR_NIGHT_BLACK, stroke=color)
button_group.append(main_btn)
# Text
if text:
text_label = label.Label(terminalio.FONT, text=text, color=text_color)
text_label.anchor_point = (0.5, 0.5)
text_label.anchored_position = (x + width//2, y + height//2)
button_group.append(text_label)
return button_group
def create_hud_element(x, y, width, height, color, alpha=0.3):
"""Create HUD-style translucent element"""
hud_group = displayio.Group()
# Calculate safe radius
safe_radius = min(width // 2, height // 2, 3)
# Background with transparency effect
if safe_radius > 0:
bg = RoundRect(x, y, width, height, safe_radius, fill=COLOR_DARK_OVERLAY, stroke=color)
else:
bg = Rect(x, y, width, height, fill=COLOR_DARK_OVERLAY, stroke=color)
hud_group.append(bg)
# Accent line
accent = Line(x, y, x + width, y, color=color)
hud_group.append(accent)
return hud_group
def create_speedometer_arc(center_x, center_y, radius, start_angle, end_angle, color, thickness=2):
"""Create speedometer-style arc"""
arc_group = displayio.Group()
# Calculate arc points
angle_step = (end_angle - start_angle) / 20
for i in range(20):
angle1 = start_angle + i * angle_step
angle2 = start_angle + (i + 1) * angle_step
x1 = center_x + int(radius * math.cos(math.radians(angle1)))
y1 = center_y + int(radius * math.sin(math.radians(angle1)))
x2 = center_x + int(radius * math.cos(math.radians(angle2)))
y2 = center_y + int(radius * math.sin(math.radians(angle2)))
line = Line(x1, y1, x2, y2, color=color)
arc_group.append(line)
return arc_group
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Display Setup with Anti-Aliasing
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
displayio.release_displays()
display_bus = FourWire(spi, command=dc_pin, chip_select=cs_pin, reset=reset_pin)
display = ST7735R(display_bus, width=SCREEN_WIDTH, height=SCREEN_HEIGHT, bgr=True, rotation=180)
# Create root group with proper background
root_group = displayio.Group()
display.root_group = root_group
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Advanced UI Components
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
class PremiumDisplay:
def __init__(self):
self.current_page = 0
self.transition_progress = 0
self.last_transition_time = 0
self.is_transitioning = False
self.speedometer_visible = False # Track speedometer visibility
# Create main display group
self.main_group = displayio.Group()
root_group.append(self.main_group)
self.setup_base_ui()
self.create_dynamic_elements()
def setup_base_ui(self):
"""Setup the base UI structure"""
# Full screen gradient background
self.bg_gradient = create_gradient_rect(0, 0, SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT,
COLOR_NIGHT_BLACK, COLOR_DEEP_BLUE, 12)
self.main_group.append(self.bg_gradient)
# Create header with advanced styling
self.create_premium_header()
# Create main content area
self.create_content_zones()
# Create bottom navigation
self.create_nav_dock()
def create_premium_header(self):
"""Create premium header with status indicators"""
self.header_group = displayio.Group()
# Header background with gradient
header_bg = create_gradient_rect(0, 0, SCREEN_WIDTH, 24,
COLOR_CHARCOAL, COLOR_NIGHT_BLACK, 4)
self.header_group.append(header_bg)
# Brand text
brand_label = label.Label(terminalio.FONT, text="NAVIGATOR",
color=COLOR_ELECTRIC_BLUE, x=4, y=8)
self.header_group.append(brand_label)
# GPS constellation indicator
self.gps_constellation = displayio.Group()
for i in range(4):
star = Circle(SCREEN_WIDTH - 20 + i*3, 8, 1, fill=COLOR_COOL_GRAY)
self.gps_constellation.append(star)
self.header_group.append(self.gps_constellation)
# Connection status
self.connection_indicator = Circle(SCREEN_WIDTH - 6, 8, 3, fill=COLOR_CRIMSON)
self.header_group.append(self.connection_indicator)
self.main_group.append(self.header_group)
def create_content_zones(self):
"""Create main content display zones"""
self.content_group = displayio.Group()
# Primary data display
self.primary_hud = create_hud_element(8, 30, SCREEN_WIDTH-16, 45, COLOR_ELECTRIC_BLUE)
self.content_group.append(self.primary_hud)
# Main value display (large, centered)
self.main_value = label.Label(terminalio.FONT, text="0.0",
color=COLOR_WARM_WHITE, x=64, y=52)
self.main_value.anchor_point = (0.5, 0.5)
self.main_value.anchored_position = (64, 52)
self.content_group.append(self.main_value)
# Unit display
self.unit_display = label.Label(terminalio.FONT, text="km/h",
color=COLOR_SILVER, x=64, y=65)
self.unit_display.anchor_point = (0.5, 0.5)
self.unit_display.anchored_position = (64, 65)
self.content_group.append(self.unit_display)
# Secondary metrics panel
self.metrics_panel = create_hud_element(8, 80, SCREEN_WIDTH-16, 32, COLOR_NEON_GREEN)
self.content_group.append(self.metrics_panel)
# Metric labels
self.metric_labels = []
for i in range(3):
metric_label = label.Label(terminalio.FONT, text="",
color=COLOR_PLATINUM, x=12, y=88 + i*8)
self.content_group.append(metric_label)
self.metric_labels.append(metric_label)
# Speedometer arc for speed page (create but don't add yet)
self.speedometer_group = displayio.Group()
self.speed_arc = create_speedometer_arc(64, 52, 35, 200, 340, COLOR_ELECTRIC_BLUE)
self.speedometer_group.append(self.speed_arc)
self.main_group.append(self.content_group)
def create_nav_dock(self):
"""Create bottom navigation dock"""
self.nav_group = displayio.Group()
# Navigation background
nav_bg = create_gradient_rect(0, SCREEN_HEIGHT-16, SCREEN_WIDTH, 16,
COLOR_CHARCOAL, COLOR_NIGHT_BLACK, 3)
self.nav_group.append(nav_bg)
# Page indicators
self.page_indicators = []
indicator_width = (SCREEN_WIDTH - 20) // NUM_PAGES
for i in range(NUM_PAGES):
x = 10 + i * indicator_width
# Create indicator button
indicator = create_modern_button(x, SCREEN_HEIGHT-12, indicator_width-2, 8,
PAGES[i]['color'], PAGES[i]['icon'])
self.nav_group.append(indicator)
self.page_indicators.append(indicator)
self.main_group.append(self.nav_group)
def create_dynamic_elements(self):
"""Create dynamic visual elements"""
# Particle system for transitions
self.particles = displayio.Group()
self.main_group.append(self.particles)
# Status indicators
self.status_group = displayio.Group()
self.main_group.append(self.status_group)
def update_gps_constellation(self, satellite_count):
"""Update GPS constellation display"""
if satellite_count is None:
satellite_count = 0
# Update constellation stars
for i, star in enumerate(self.gps_constellation):
if i < min(satellite_count, 4):
star.fill = COLOR_NEON_GREEN
else:
star.fill = COLOR_COOL_GRAY
def update_connection_status(self, has_fix):
"""Update connection status indicator"""
if has_fix:
self.connection_indicator.fill = COLOR_NEON_GREEN
else:
self.connection_indicator.fill = COLOR_CRIMSON
def show_speedometer(self, show=True):
"""Show or hide speedometer with proper management"""
if show and not self.speedometer_visible:
try:
self.content_group.append(self.speedometer_group)
self.speedometer_visible = True
except ValueError:
# Already added, just update flag
self.speedometer_visible = True
elif not show and self.speedometer_visible:
try:
self.content_group.remove(self.speedometer_group)
self.speedometer_visible = False
except ValueError:
# Already removed, just update flag
self.speedometer_visible = False
def transition_to_page(self, new_page):
"""Smooth transition between pages"""
if new_page != self.current_page:
self.current_page = new_page
self.is_transitioning = True
self.transition_progress = 0
# Update colors and theme
page_config = PAGES[new_page]
# Update HUD colors
self.primary_hud[1].stroke = page_config['color'] # Border
self.metrics_panel[1].stroke = page_config['accent'] # Border
# Update main value color
self.main_value.color = page_config['color']
# Handle speedometer visibility
if new_page == 0: # VELOCITY page
self.show_speedometer(True)
else:
self.show_speedometer(False)
def update_display_data(self, speed, distance, avg_speed, peak_speed, elapsed_time, gps_obj):
"""Update all display data"""
page_config = PAGES[self.current_page]
if self.current_page == 0: # VELOCITY
self.main_value.text = f"{speed * 3.6:.1f}"
self.unit_display.text = "km/h"
self.metric_labels[0].text = f"Peak: {peak_speed * 3.6:.1f} km/h"
self.metric_labels[1].text = f"Avg: {avg_speed * 3.6:.1f} km/h"
self.metric_labels[2].text = f"Range: {distance/1000:.1f} km"
elif self.current_page == 1: # DISTANCE
self.main_value.text = f"{distance/1000:.2f}"
self.unit_display.text = "kilometers"
self.metric_labels[0].text = f"Time: {format_time(elapsed_time)}"
self.metric_labels[1].text = f"Speed: {speed * 3.6:.1f} km/h"
self.metric_labels[2].text = f"Efficiency: {(distance/1000)/(elapsed_time/3600):.1f} km/h" if elapsed_time > 0 else "Efficiency: 0.0 km/h"
elif self.current_page == 2: # ANALYTICS
self.main_value.text = f"{avg_speed * 3.6:.1f}"
self.unit_display.text = "avg km/h"
self.metric_labels[0].text = f"Distance: {distance/1000:.2f} km"
self.metric_labels[1].text = f"Duration: {format_time(elapsed_time)}"
self.metric_labels[2].text = f"Max Speed: {peak_speed * 3.6:.1f} km/h"
elif self.current_page == 3: # CHRONOS
self.main_value.text = format_time(elapsed_time)
self.unit_display.text = "elapsed"
self.metric_labels[0].text = f"Distance: {distance/1000:.2f} km"
self.metric_labels[1].text = f"Current: {speed * 3.6:.1f} km/h"
self.metric_labels[2].text = f"Average: {avg_speed * 3.6:.1f} km/h"
elif self.current_page == 4: # TELEMETRY
self.main_value.text = f"{gps_obj.satellites or 0}"
self.unit_display.text = "satellites"
self.metric_labels[0].text = f"Lat: {format_coordinate(gps_obj.latitude, True)}"
self.metric_labels[1].text = f"Lon: {format_coordinate(gps_obj.longitude, False)}"
self.metric_labels[2].text = f"Alt: {gps_obj.altitude_m:.0f}m" if gps_obj.altitude_m else "Alt: N/A"
# Update GPS indicators
self.update_gps_constellation(gps_obj.satellites)
self.update_connection_status(gps_obj.has_fix)
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Initialize Premium Display
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
premium_display = PremiumDisplay()
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# State Variables
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
last_encoder = encoder.position
page = 0
last_button_time = 0
button_debounce = 0.5
start_time = time.monotonic()
prev_lat = None
prev_lon = None
last_gps_log = 0
gps_log_interval = 3.0 # More frequent logging
total_distance = 0.0
peak_speed = 0.0
update_counter = 0
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Main Loop
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
print("╔════════════════════════════════════════╗")
print("║ PREMIUM GPS NAVIGATOR v2.0 ║")
print("║ Professional Trip Computer ║")
print("╚════════════════════════════════════════╝")
while True:
current_time = time.monotonic()
update_counter += 1
# Update GPS data
gps.update()
# Enhanced GPS logging
if current_time - last_gps_log >= gps_log_interval:
log_gps_telemetry(gps)
last_gps_log = current_time
# Handle encoder with smooth transitions
pos = encoder.position
if pos != last_encoder:
new_page = (page + (1 if pos > last_encoder else -1)) % NUM_PAGES
premium_display.transition_to_page(new_page)
page = new_page
last_encoder = pos
print(f"🔄 Switched to {PAGES[page]['name']} mode")
# Handle button press with haptic-like feedback
if not button.value and (current_time - last_button_time > button_debounce):
total_distance = 0.0
peak_speed = 0.0
start_time = current_time
prev_lat = None
prev_lon = None
last_button_time = current_time
print("🔄 TRIP RESET - All metrics cleared")
print("=" * 40)
# Visual feedback
while not button.value:
time.sleep(0.01)
# Calculate metrics
speed = gps.speed_knots * 0.514444 if gps.has_fix else 0.0
# Smart distance calculation with noise filtering
if gps.has_fix and prev_lat is not None:
d = haversine(prev_lat, prev_lon, gps.latitude, gps.longitude)
if d > 0.5 and d < 100: # Filter GPS noise and jumps
total_distance += d
# Update peak speed
if speed > peak_speed:
peak_speed = speed
# Store position
if gps.has_fix:
prev_lat = gps.latitude
prev_lon = gps.longitude
# Calculate derived metrics
elapsed = current_time - start_time
avg_speed = (total_distance / elapsed) if elapsed > 0 else 0.0
# Update premium display
premium_display.update_display_data(speed, total_distance, avg_speed,
peak_speed, elapsed, gps)
# Smooth 20Hz update rate for premium feel
time.sleep(0.05)
# End of premium GPS navigator
Building a GPS Speedometer with RP2040-Zero
*PCBWay community is a sharing platform. We are not responsible for any design issues and parameter issues (board thickness, surface finish, etc.) you choose.

Raspberry Pi 5 7 Inch Touch Screen IPS 1024x600 HD LCD HDMI-compatible Display for RPI 4B 3B+ OPI 5 AIDA64 PC Secondary Screen(Without Speaker)
BUY NOW- Comments(0)
- Likes(1)
-
 Sunarno Budi Santoso
Jul 15,2025
Sunarno Budi Santoso
Jul 15,2025
- 0 USER VOTES
- YOUR VOTE 0.00 0.00
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
 More by Inaki Iturriaga
More by Inaki Iturriaga
-
 Battery-Powered ESP32-CAM Continuous Video Recorder
OverviewThis project transforms an ESP32-CAM module into a standalone, battery-powered video recordi...
Battery-Powered ESP32-CAM Continuous Video Recorder
OverviewThis project transforms an ESP32-CAM module into a standalone, battery-powered video recordi...
-
 GPS Mobile Beacon
Building a GPS Emergency Beacon: A DIY TutorialWelcome to our latest DIY project: creating a GPS Eme...
GPS Mobile Beacon
Building a GPS Emergency Beacon: A DIY TutorialWelcome to our latest DIY project: creating a GPS Eme...
-
 Wireless RFID Card Copier.
Wireless RFID Card CopierIn today's digital world, security and accessibility are of paramount impor...
Wireless RFID Card Copier.
Wireless RFID Card CopierIn today's digital world, security and accessibility are of paramount impor...
-
 Piezo Alert System.
Within the fast-evolving sphere of security tools and home automation, creativity often paves the wa...
Piezo Alert System.
Within the fast-evolving sphere of security tools and home automation, creativity often paves the wa...
-
 Wifi Weather Station - Sensors board
WiFi Weather Station - Sensor unitIn our digital era, many electronics projects integrate diverse se...
Wifi Weather Station - Sensors board
WiFi Weather Station - Sensor unitIn our digital era, many electronics projects integrate diverse se...
-
 Building a GPS Speedometer with RP2040-Zero
Build a Feature-Packed GPS Speedometer with an RP2040This project guide will walk you through buildi...
Building a GPS Speedometer with RP2040-Zero
Build a Feature-Packed GPS Speedometer with an RP2040This project guide will walk you through buildi...
-
 RC Receiver
Build Your Own RC ReceiverHarnessing advanced electronics and precise control systems, the RC Receiv...
RC Receiver
Build Your Own RC ReceiverHarnessing advanced electronics and precise control systems, the RC Receiv...
-
 Universal RC Controller
Build Your Own Universal RC RemoteHarnessing the power of custom PCBs and wireless communication, th...
Universal RC Controller
Build Your Own Universal RC RemoteHarnessing the power of custom PCBs and wireless communication, th...
-
 Continuous GPS Tracker
This compact and efficient tracker provides real-time location updates, making it ideal for surveill...
Continuous GPS Tracker
This compact and efficient tracker provides real-time location updates, making it ideal for surveill...
-
 Air Quality Monitor
Welcome to our DIY tutorial on assembling an Air Quality Monitoring Device. This project is perfect ...
Air Quality Monitor
Welcome to our DIY tutorial on assembling an Air Quality Monitoring Device. This project is perfect ...
-
 Automatic Watch Winder
Automatic Watch WinderIn the realm of luxury timepieces and watch aficionados, an automatic watch is...
Automatic Watch Winder
Automatic Watch WinderIn the realm of luxury timepieces and watch aficionados, an automatic watch is...
-
 Handheld GPS
Within the swiftly advancing realm of portable technology and travel essentials, innovation often sh...
Handheld GPS
Within the swiftly advancing realm of portable technology and travel essentials, innovation often sh...
-
 Dual Motor Controller for Model Robotics
In the thrilling world of robotics and DIY engineering, innovation continues to soar to new heights....
Dual Motor Controller for Model Robotics
In the thrilling world of robotics and DIY engineering, innovation continues to soar to new heights....
-
 Altitude Indicator with Beeper for Rocketry
Altitude Indicator for Model RocketryIn our ever-advancing technological landscape, countless projec...
Altitude Indicator with Beeper for Rocketry
Altitude Indicator for Model RocketryIn our ever-advancing technological landscape, countless projec...
-
 Wifi Weather Station - Display unit
WiFi Weather Station - Display UnitIn this technologically advanced age, countless electronics proje...
Wifi Weather Station - Display unit
WiFi Weather Station - Display UnitIn this technologically advanced age, countless electronics proje...
-
 Positon Breakout Board
Position Sensors Breakout Board In today's era of advanced technology, many electronics projects req...
Positon Breakout Board
Position Sensors Breakout Board In today's era of advanced technology, many electronics projects req...
-
 Ambient Sensors Breakout Board
In today's world, electronics projects often require the integration of multiple sensors to collect ...
Ambient Sensors Breakout Board
In today's world, electronics projects often require the integration of multiple sensors to collect ...
-
 Infrared Launch Controller
IntroductionHave you ever wanted to remotely launch a rocket, drone or other device using infrared t...
Infrared Launch Controller
IntroductionHave you ever wanted to remotely launch a rocket, drone or other device using infrared t...
-
A Compact Charging Breakout Board For Waveshare ESP32-C3
477 3 4 -
AI-driven LoRa & LLM-enabled Kiosk & Food Delivery System
488 2 0 -
-
-
-
ESP32-C3 BLE Keyboard - Battery Powered with USB-C Charging
683 0 1 -
-
mammoth-3D SLM Voron Toolhead – Manual Drill & Tap Edition
672 0 1 -
-
AEL-2011 Power Supply Module
1343 0 2 -
AEL-2011 50W Power Amplifier
1224 0 2